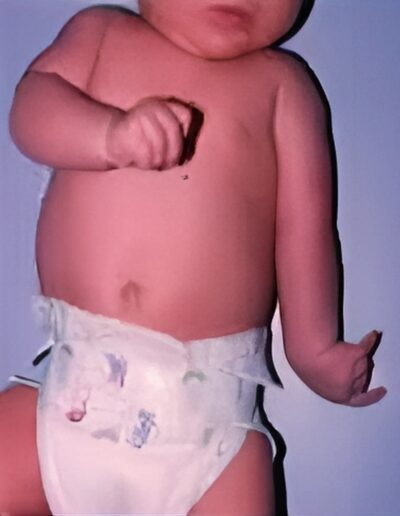
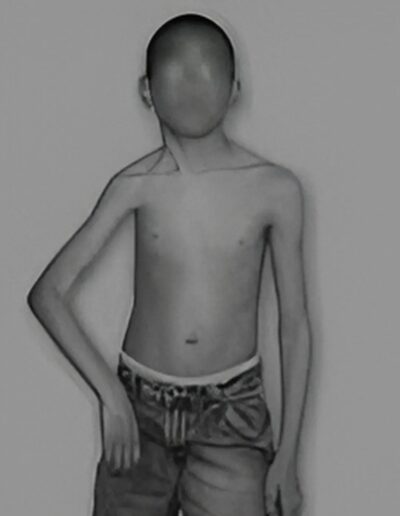
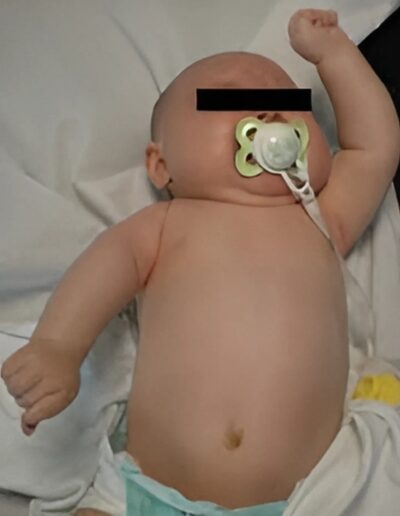
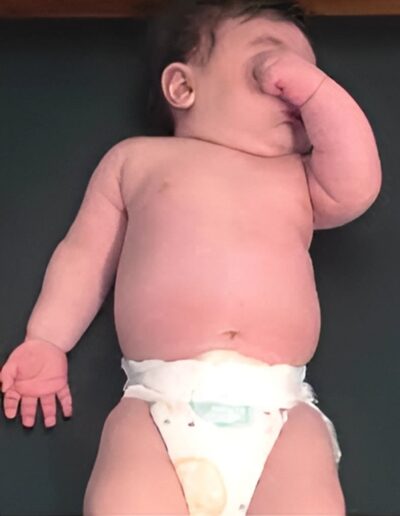
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that run from the spinal cord, through the neck, to the arm. Brachial plexus birth injury refers to damage to the brachial plexus that occurs at birth, and may be related to a difficult labor and delivery.
During delivery of large babies, or smaller babies in breech presentation, the nerves of the brachial plexus may be stretched and injured. Some risk factors associated with brachial plexus birth injury include a long, difficult labor, a larger-than-normal infant, gestational diabetes, maternal obesity and breech presentation.
The symptoms can vary widely in severity based on the extent of the damage. There is incomplete sensory and motor function in the affected arm. The most common (and least severe) presentation is Erb’s palsy, in which the shoulder is internally rotated, the elbow extended, and the hand and wrist function normally.
The most severe presentation of brachial plexus birth injury, also known as global palsy, presents with complete paralysis of the affected arm, without function in the shoulder, elbow, forearm, wrist nor hand. There are intermediate presentations between Erb’s and global palsy.
Initial evaluation of patients with brachial plexus birth injury should take place within the first 1-2 months of life, and it should be performed at a center that specializes in the care of brachial plexus injuries. Despite the fact that many cases will recover spontaneously, early therapy with a pediatric occupational/physical therapist is critical to prevent permanent joint deformities from developing. If spontaneous recovery does not occur, surgery may be required to repair or reconstruct the damaged nerves.
In the most severe cases, this type of operation may be considered as early as 3 months of age. As the child grow, surgery may be considered to improve weak muscles and correct joint deformities; usually tendon transfers and bone repositioning.
Cardiology is the medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to the heart and blood vessels. Basic knowledge of cardiology includes understanding the anatomy and function of the heart, the various cardiovascular diseases, risk factors for heart disease, diagnostic techniques such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) and echocardiograms, treatment options including medications, interventions, and surgeries, and preventive measures to maintain heart health.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, and some individuals with heart disease may not experience any symptoms until a more advanced stage. If you are experiencing any concerning symptoms, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.