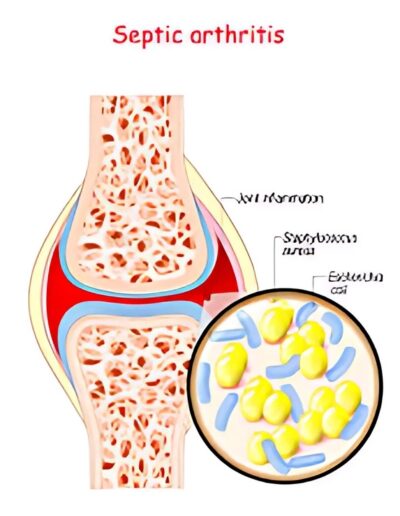
Septic arthritis is an infection in the joint fluid (also known as synovial fluid) and joint tissues. The infection usually reaches the joints though the bloodstream, although some joints may become infected after surgery or injury of an involved joint, which can expose the joint space to germs or infection.
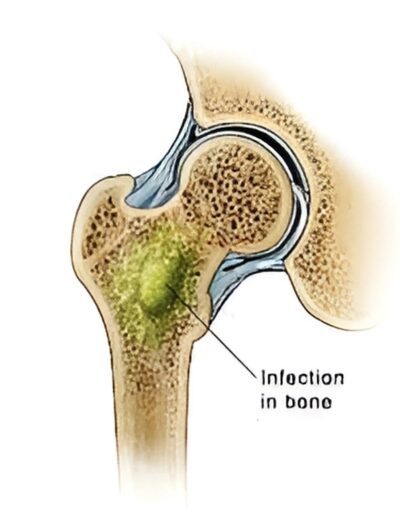
In rare instances, an infection of the bone can spread to an adjacent joint causing septic arthritis. Bacteria, fungus, or viruses are capable of infecting the joint, although “septic arthritis” is typically used to describe non-viral causes of joint infections, which are usually caused by bacteria.
In most children, septic arthritis only affects one joint in the body. The most common sites for septic arthritis include the:
Symptoms of septic arthritis vary from child to child and may differ depending on which joint is affected, the age of the child, and the type of organism causing the infection.
Septic arthritis typically has a fast onset with symptoms progressing to the point of severe pain and immobility of the affected joint within hours.
Common symptoms include:
Specific treatment for septic arthritis will be determined by your child’s doctor based on:
Septic arthritis usually requires treatment with antibiotics, which are often given intravenously to ensure prompt response to therapy. Antibiotics are only effective if your child’s condition is caused by a bacteria.
If your child’s infection is caused by fungi, he will need antifungal medications.
If a viral infection caused your child’s septic arthritis, the virus will usually need to run its course without treatment, although medications can be used to help alleviate pain.
In some cases, the infected joint must be drained and cleaned because antibiotics cannot penetrate deep enough into a severely infected joint. This may require drainage by a needle, tube or surgery.
Other symptom-based treatments may include:
Cardiology is the medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to the heart and blood vessels. Basic knowledge of cardiology includes understanding the anatomy and function of the heart, the various cardiovascular diseases, risk factors for heart disease, diagnostic techniques such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) and echocardiograms, treatment options including medications, interventions, and surgeries, and preventive measures to maintain heart health.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, and some individuals with heart disease may not experience any symptoms until a more advanced stage. If you are experiencing any concerning symptoms, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.