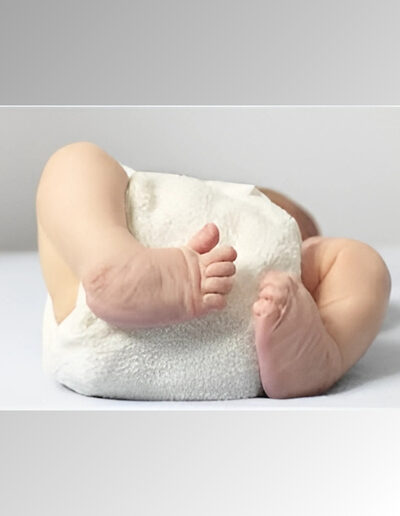
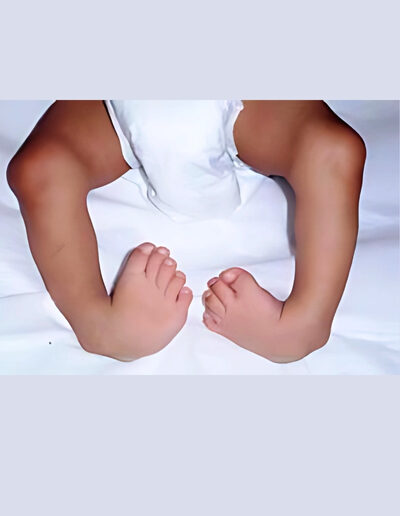
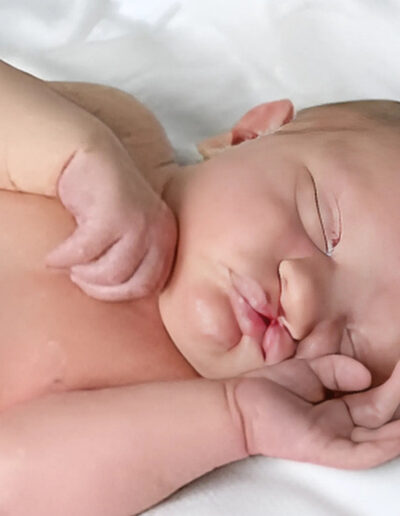



About 3 to 4 percent of babies are born with some type of birth defect. A birth defect is a health problem or a physical abnormality. It can be very mild or severe. Some birth defects are life-threatening, in which case a baby may only live for a few months. Birth defects are also referred to as “congenital anomalies” or “congenital abnormalities.”
The most common birth defects are:
Most birth defects are caused by genetic or environmental factors or a combination of the two (multifactorial birth defects). In most cases, however, the cause is unknown.
Genetic or inherited causes include:
An environmental cause can include a drug, alcohol or a disease the mother has that can increase the chance for the baby to be born with a birth defect. An agent that can cause a birth defect is known as a teratogen.
Multifactorial birth defects are caused by a combination of genes and environmental exposures. In other words, a person can inherit a gene that increases sensitivity to an environmental trigger. Examples include Fibular hemimelia, tibial hemimelia, CFFD and neural tube defects.
Some birth defects can be diagnosed before birth through ultrasound, amniocentesis or chronic villus sampling (CVS). Most women have blood tests to screen for their risk of having a baby with a specific birth defect, such as Down syndrome and spina bifida. While it does not usually lead to a cure for the baby’s birth defect, prenatal diagnosis can prepare the parents emotionally and help them prepare for a child with a birth defect.
In other cases a birth defect is diagnosed after birth through physical examination or a blood test that screens for several disorders in newborns.
Gene therapy replaces a gene that is either missing or defective. Severe combined immunodeficiency diseases (SCID) are a group of very rare diseases for which gene therapy has been used.
Enzymes are proteins for which genes code. So when a gene is mutated and does not produce the gene product, an enzyme is missing or defective. One way to treat this type of genetic defect is to replace the enzyme that the gene is not producing. An example of a condition for which enzyme replacement therapy has been developed is Gaucher disease.
Surgical treatment Limb reconstruction surgery to correct limb deficiency, limb shortening ,Deformity joint reconstruction for good functional and cosmetic outcome
Cardiology is the medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to the heart and blood vessels. Basic knowledge of cardiology includes understanding the anatomy and function of the heart, the various cardiovascular diseases, risk factors for heart disease, diagnostic techniques such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) and echocardiograms, treatment options including medications, interventions, and surgeries, and preventive measures to maintain heart health.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, and some individuals with heart disease may not experience any symptoms until a more advanced stage. If you are experiencing any concerning symptoms, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.