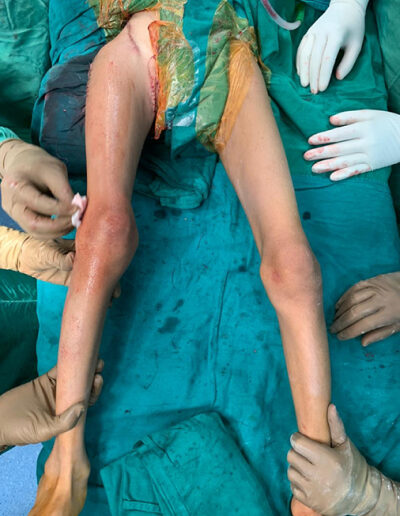
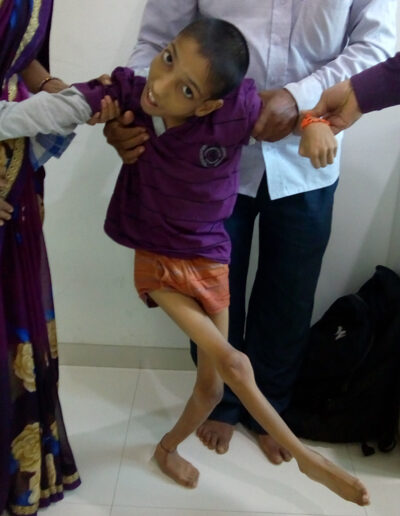

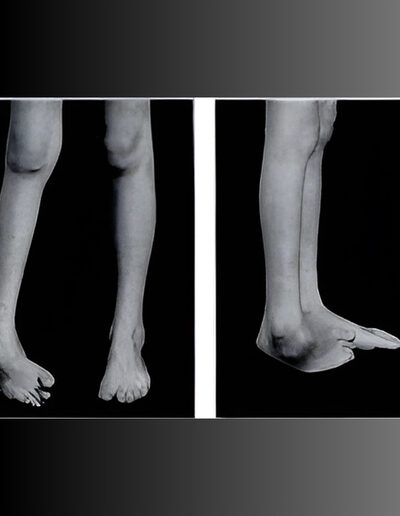
Children with cerebral palsy may have a number of bone, joint and muscle problems that affect their walking (gait).
Before the medical team decides on a surgical treatment for your child with a gait disorder, he will undergo a gait analysis. Gait analysis allows our surgeons to treat your child with more precision, and makes it possible to address all of your child’s gait problems at once.
Most children with cerebral palsy with gait disorders have issues which need to be addressed either with surgery, bracing or medications at multiple levels. We design surgeries to correct as many bony and soft tissue deformities as possible during a single trip to the operating room.
In the case of children with involvement of both legs, this involves the use of two surgical teams, allowing for a more comprehensive approach to treatment. After the one surgical event, your child will only require one course of rehabilitation, rather than multiple surgical episodes and multiple courses of rehabilitation and recovery.
Muscle lengthening procedures may be performed surgically to improve joint motion and gait, and to prevent deformities. Lengthening procedures can also be used to decrease the need for bony surgery in younger children, and reduce tone on a more permanent basis than botulinum toxin.
Tendon transfers allow muscles to be partially transferred to a different location in the joint, which can balance the forces across a joint in a better way.
Bony reconstruction allows for direct restoration of anatomic position of joints, or relief of rotational abnormalities which result in brace intolerance.
In cases where the deformity is too severe to be managed with simple realignment, fusion can provide a durable option to provide long term support of a child’s skeleton.
Cardiology is the medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases related to the heart and blood vessels. Basic knowledge of cardiology includes understanding the anatomy and function of the heart, the various cardiovascular diseases, risk factors for heart disease, diagnostic techniques such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) and echocardiograms, treatment options including medications, interventions, and surgeries, and preventive measures to maintain heart health.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, and some individuals with heart disease may not experience any symptoms until a more advanced stage. If you are experiencing any concerning symptoms, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.